Carbon emission reporting and carbon accounting
What is carbon emission reporting?
Carbon emission reporting is the systematic process of measuring, documenting, and disclosing an organization's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It's also known under the names carbon accounting- and greenhouse gas reporting.
This process involves quantifying the carbon footprint of an organization, which includes all GHG emissions resulting from its operations, products, and services.
Why are carbon accounting and carbon emission reporting important?
Carbon emission reporting is slowly progressing into a crucial aspect of modern business practices. It serves multiple purposes that benefit both organizations and society at large:
Environmental Responsibility: It helps organizations understand and manage their environmental impact.Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions now require carbon reporting for certain businesses.
Stakeholder Transparency: Investors, customers, and partners increasingly demand climate-related disclosures.
Risk Management: Identifying emission sources can highlight potential regulatory or reputational risks.
Competitive Advantage: Demonstrating environmental stewardship can enhance brand value and market position.
What needs to be reported
Understanding what needs to be reported on is critical for organizations aiming to meet regulatory requirements, align with industry standards, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
One of the most widely recognized frameworks for emissions reporting categorizes greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions into three distinct scopes: Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3.
Scope 1: Direct emissions
Scope 1 encompasses direct emissions from sources that are owned or controlled by the organization, such as fuel combustion in company-owned vehicles or facilities.
- Emissions from sources owned or controlled by the organization
- Examples: On-site fuel combustion, company vehicle emissions
Scope 2: Electricity indirect emissions
Scope 2 covers indirect emissions associated with the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, or cooling consumed by the organization.
- Emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling
- Calculated using location-based or market-based methods
Scope 3: Other indirect emissions
Scope 3 extends beyond the boundaries of the organization to include all other indirect emissions resulting from activities across its value chain, such as those from suppliers, transportation, product use, and waste disposal.
- All other indirect emissions in a company's value chain
- Categories include purchased goods and services, business travel, employee commuting, waste disposal, etc.
Carbon emission reporting regulations
To ensure comparability, credibility, and consistency in carbon reporting, organizations increasingly align their disclosures with globally recognized frameworks and standards. These frameworks provide structured guidance on methodologies, reporting boundaries, and disclosure requirements, establishing a common language for carbon reporting across industries and regions.
Widely used reporting standards and frameworks
GHG Protocol (Greenhouse Gas protocol):
A globally recognized standard for measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Scope: Covers three scopes of emissions: scope 1 (direct emissions), scope 2 (indirect emissions from purchased energy), and scope 3 (all other indirect emissions).
CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project):
An international nonprofit organization that provides an environmental impact disclosure system for the private and public sectors.
- Scope: Collects data on climate change, deforestation, water security, and plastic use.
TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures):
A global organization that developed recommendations for climate-related financial disclosures.
- Scope: Focuses on governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets related to climate risks and opportunities.
SBTi (Science Based Targets initiative):
An initiative that provides guidance for science-based emission reduction targets aligned with limiting global temperature rise.
- Scope: Covers greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets for companies.
Carbon accounting software
By leveraging a carbon emission platform, businesses not only meet their carbon reporting obligations more effectively but also gain valuable insights to drive meaningful sustainability improvements and competitive advantage.
Modern carbon reporting increasingly relies on specialized software solutions that offer:
- Automated data collection: Integration with existing systems to streamline data gathering.
- Real-time monitoring: Continuous tracking of emissions data.
- Compliance management: Features to ensure adherence to relevant reporting standards.
- Analytics and scenario planning: Capabilities to model different emission reduction strategies.
Measure, reduce and report your carbon footprint with a software solution
An example is the Master Sustainability ESG platform in which seamless and end-to-end management of carbon emissions is possible. Including comprehensive ESG goal management, one-click CSRD - ESRS regulator reporting, integrations and custom API's, sustainability KPI management and much more.
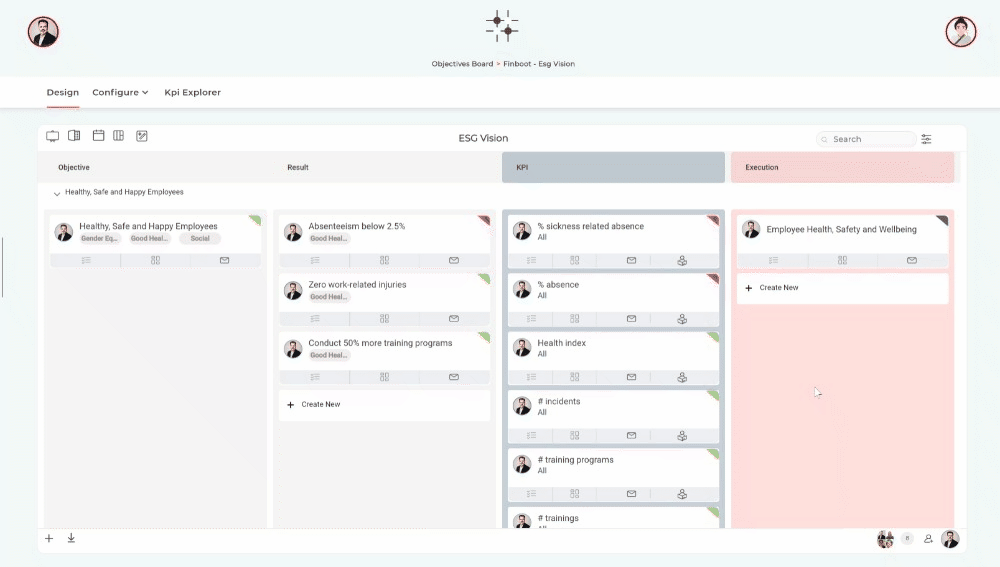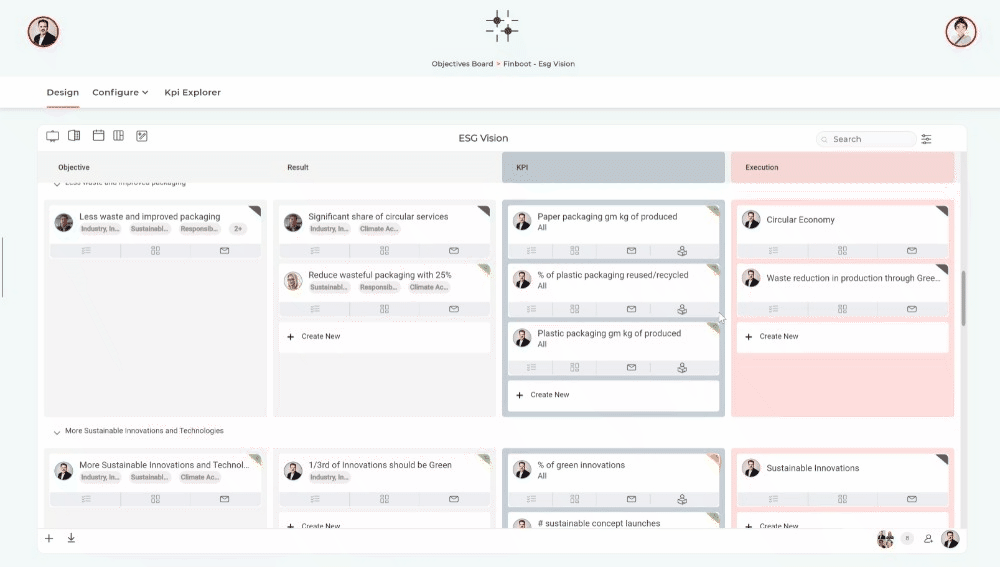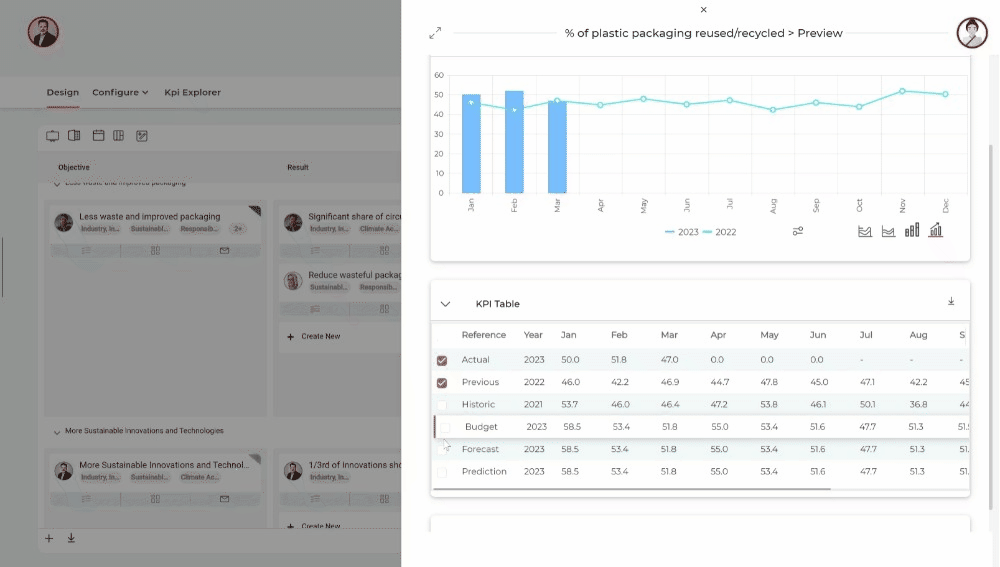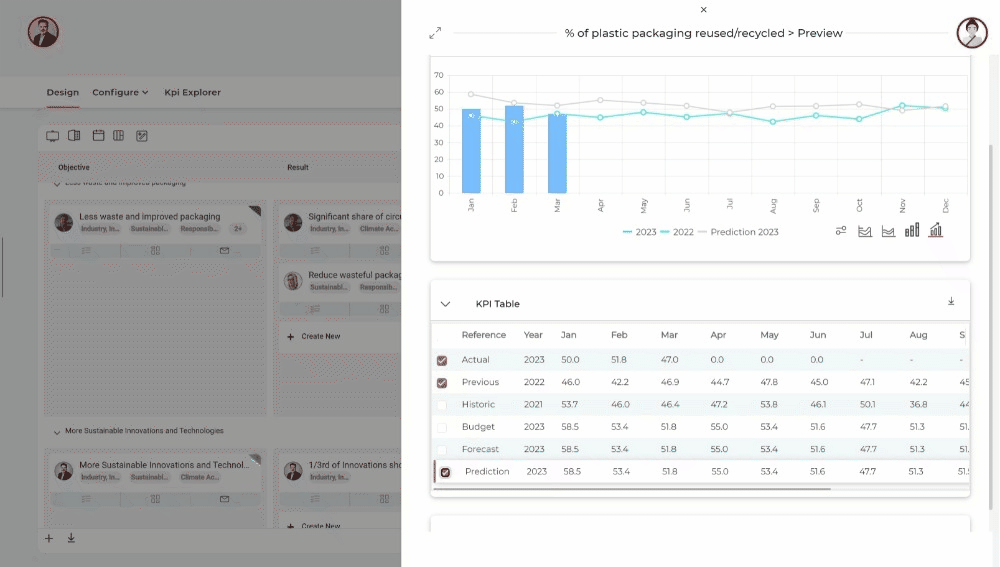
Start mastering carbon accounting
Start with Carbon Emission reporting and Master Sustainability
Take a look at a carbon emission reporting platform (infographic)
This guide not only provides insights into Carbon Emission and its relationship with CSRD, but also presents an integrated software solution designed to outperform industry standards.
Our tool simplifies the process of carbon emissions reporting, making it easier to comply with standards and adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes.